이득우의 게임 수학
구 영역 대신 박스 영역을 사용하면 좀 더 정교한 절두체 컬링을 수행할 수 있다.
메시 데이터로부터 박스 영역을 생성하는 방법은 간단하다.
- 메시를 구성하는 점을 순회하면서 각 차원의 최댓값과 최솟값을 갱신해주면 된다.
- n개의 정점이 있을 때, O(n) 시간에 구할 수 있다.
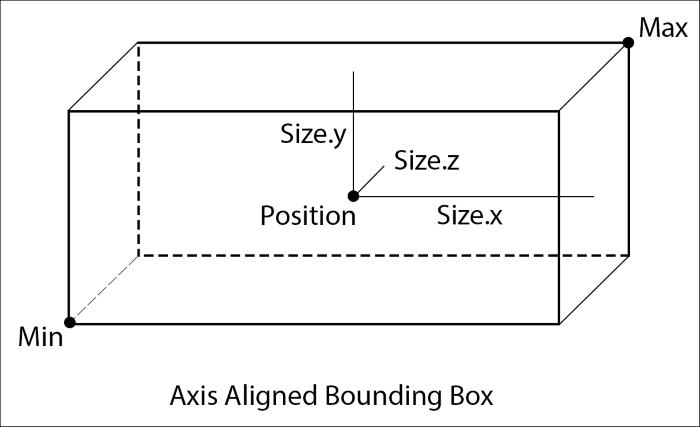
이렇게 생성된 박스 영역을 기저 축이 정렬되어 있다는 의미에서 AABB 바운딩 볼륨이라고 한다.
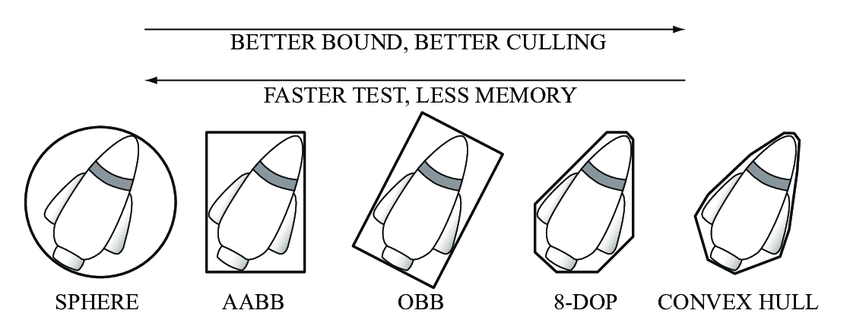
구나 AABB 말고도 성능과 효율의 Trade-off에 따라 다양한 바운딩 볼륨이 존재한다.
책의 예제인 CK소프트렌더러에 정의된 AABB는 다음과 같다.
// 책의 예제인 CK소프트렌더러에 정의된 AABB
struct Box
{
public:
FORCEINLINE constexpr Box() = default;
FORCEINLINE constexpr Box(const Box& InBox) : Min(InBox.Min), Max(InBox.Max) { }
FORCEINLINE constexpr Box(const Vector3& InMinVector, const Vector3& InMaxVector) : Min(InMinVector), Max(InMaxVector) { }
Box(const vector<Vector3> InVertices);
FORCEINLINE constexpr bool Intersect(const Box& InBox) const
{
if ((Min.X > InBox.Max.X) || (InBox.Min.X > Max.X))
{
return false;
}
if ((Min.Y > InBox.Max.Y) || (InBox.Min.Y > Max.Y))
{
return false;
}
if ((Min.Z > InBox.Max.Z) || (InBox.Min.Z > Max.Z))
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
FORCEINLINE constexpr bool IsInside(const Box& InBox) const
{
return (IsInside(InBox.Min) && IsInside(InBox.Max));
}
FORCEINLINE constexpr bool IsInside(const Vector3& InVector) const
{
return ((InVector.X >= Min.X) && (InVector.X <= Max.X) && (InVector.Y >= Min.Y) && (InVector.Y <= Max.Y) && (InVector.Z >= Min.Z) && (InVector.Z <= Max.Z));
}
FORCEINLINE constexpr Box operator +=(const Vector3& InVector)
{
Min.X = Math::Min(Min.X, InVector.X);
Min.Y = Math::Min(Min.Y, InVector.Y);
Min.Z = Math::Min(Min.Z, InVector.Z);
Max.X = Math::Max(Max.X, InVector.X);
Max.Y = Math::Max(Max.Y, InVector.Y);
Max.Z = Math::Max(Max.Z, InVector.Z);
return *this;
}
FORCEINLINE constexpr Box operator +=(const Box& InBox)
{
Min.X = Math::Min(Min.X, InBox.Min.X);
Min.Y = Math::Min(Min.Y, InBox.Min.Y);
Min.Z = Math::Min(Min.Z, InBox.Min.Z);
Max.X = Math::Max(Max.X, InBox.Max.X);
Max.Y = Math::Max(Max.Y, InBox.Max.Y);
Max.Z = Math::Max(Max.Z, InBox.Max.Z);
return *this;
}
FORCEINLINE constexpr Vector3 GetSize() const
{
return (Max - Min);
}
FORCEINLINE constexpr Vector3 GetExtent() const
{
return GetSize() * 0.5f;
}
...
public:
Vector3 Min;
Vector3 Max;
};
메시 정보로부터 AABB 바운딩 볼륨을 생성하는 부분은 다음과 같다.
- 메시를 구성하는 점을 순회하면서 각 차원의 최댓값과 최솟값을 갱신한다.
// 책의 예제인 CK소프트렌더러에서 메시 정보를 통해 AABB 바운딩 볼륨을 생성하는 부분
Box::Box(const vector<Vector3> InVertices)
{
for (const auto& v : InVertices)
{
*this += v;
}
}
이제 AABB 영역과 평면과의 판정은 어떻게 진행하는지 알아본다.
AABB와 평면의 법선 벡터의 x, y, z, 각 축의 요소를 나눠서 생각해 볼 때, 법선 벡터의 요소가 음수일 때는 AABB 요소의 최댓값이 평면과 가장 가깝고, 법선 벡터의 요소가 양수일 때는 AABB 요소의 최댓값이 평면과 가장 가깝게 된다.
- 예를 들어 법선 벡터의 부호가 (-, +, -)라면, 가장 가까운 AABB의 좌표는 (Max, Min, Max)가 된다.
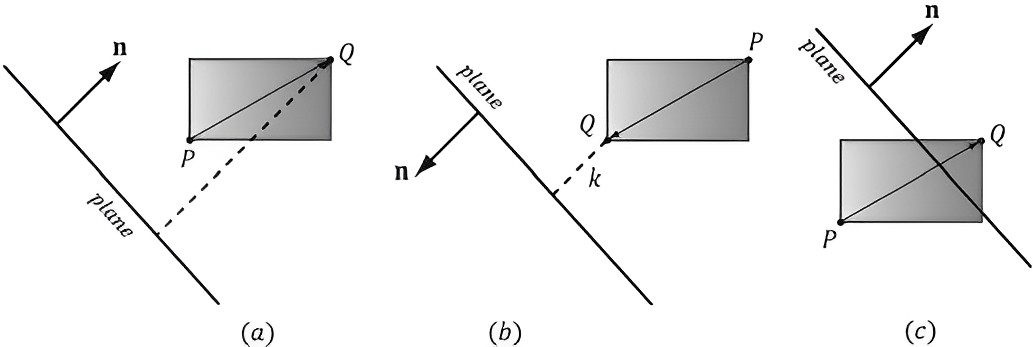
평면에서 가장 가까운 AABB 좌표와 평면과의 차이를 측정했을 때 그 값이 양수라면, AABB 영역은 완전히 평면의 바깥에 있다고 할 수 있다.
평면에서 가장 가까운 AABB 좌표와 평면과의 차이가 음수일 때, 현재 AABB 좌표의 정반대에 있는 점과 평면을 다시 테스트해 겹치는지 확인한다.
- 이때, 정반대 점과의 값이 양수라면 AABB 영역과 평면은 겹친다.
- 정반대 점과의 값이 음수라면 AABB 영역은 평면 안에 있다고 할 수 있다.
// 책의 예제인 CK소프트렌더러에서 AABB 바운딩 볼륨을 통해 절두체 컬링을 탐지하는 로직
FORCEINLINE constexpr BoundCheckResult Frustum::CheckBound(const Box& InBox) const
{
for (const auto& p : Planes)
{
// 평면의 법선 벡터 요소들의 부호에 따라 AABB의 점과 정반대 점의 좌표를 구한다.
Vector3 nPoint = InBox.Max, pPoint = InBox.Min;
if (0.f <= p.Normal.X) { nPoint.X = InBox.Min.X; pPoint.X = InBox.Max.X; }
if (0.f <= p.Normal.Y) { nPoint.Y = InBox.Min.Y; pPoint.Y = InBox.Max.Y; }
if (0.f <= p.Normal.Z) { nPoint.Z = InBox.Min.Z; pPoint.Z = InBox.Max.Z; }
if (0.f < p.Distance(nPoint))
{
return BoundCheckResult::Outside;
}
if (p.Distance(nPoint) <= 0.f && 0.f <= p.Distance(pPoint))
{
return BoundCheckResult::Intersect;
}
}
return BoundCheckResult::Inside;
}
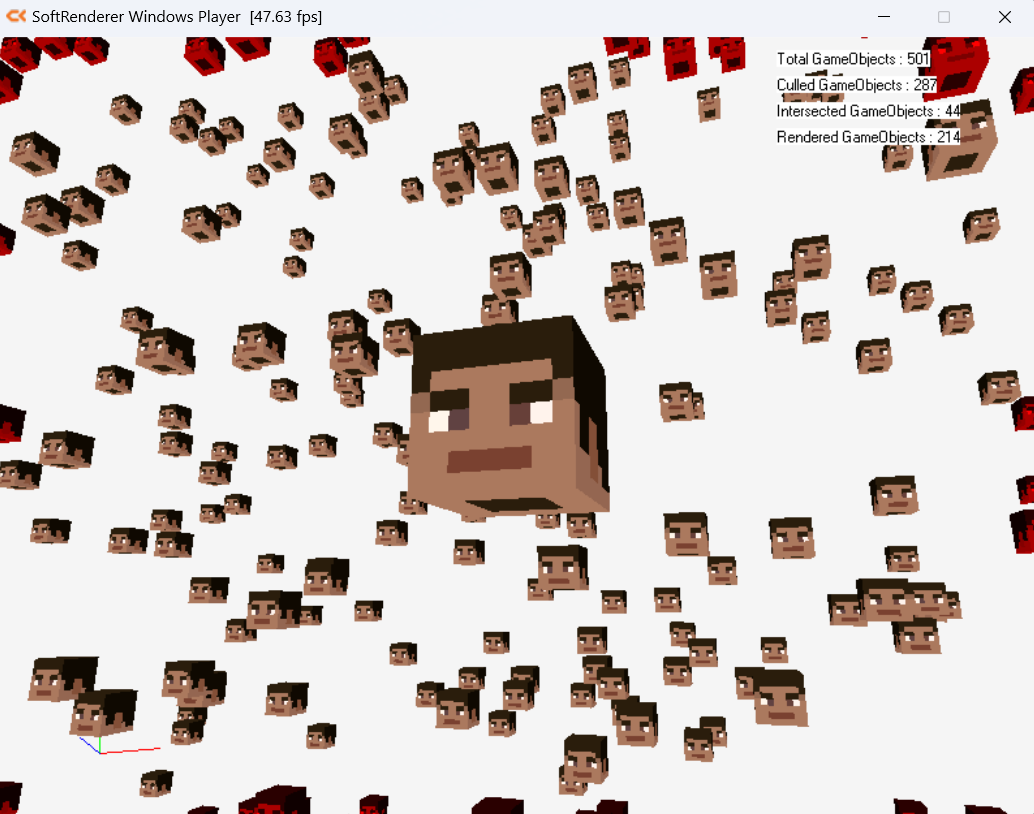
AABB 바운딩 볼륨을 절두체 컬링 판정에 사용했다.
// 책의 예제인 CK소프트렌더러에서 렌더링 로직을 담당하는 함수
void SoftRenderer::Render3D()
{
...
// 렌더링 로직의 로컬 변수
const Matrix4x4 pvMatrix = mainCamera.GetPerspectiveViewMatrix();
for (auto it = g.SceneBegin(); it != g.SceneEnd(); ++it)
{
...
// 렌더링에 필요한 게임 오브젝트의 주요 레퍼런스를 얻기
const Mesh& mesh = g.GetMesh(gameObject.GetMeshKey());
const TransformComponent& transform = gameObject.GetTransform();
// 최종 행렬 계산
Matrix4x4 finalMatrix = pvMatrix * transform.GetModelingMatrix();
LinearColor finalColor = gameObject.GetColor();
// 최종 변환 행렬로부터 평면의 방정식과 절두체 생성
Matrix4x4 finalTransposedMatrix = finalMatrix.Transpose();
std::array<Plane, 6> frustumPlanesFromMatrix = {
Plane(-(finalTransposedMatrix[3] - finalTransposedMatrix[1])), // Up
Plane(-(finalTransposedMatrix[3] + finalTransposedMatrix[1])), // Bottom
Plane(-(finalTransposedMatrix[3] - finalTransposedMatrix[0])), // Right
Plane(-(finalTransposedMatrix[3] + finalTransposedMatrix[0])), // Left
Plane(-(finalTransposedMatrix[3] - finalTransposedMatrix[2])), // Far
Plane(-(finalTransposedMatrix[3] + finalTransposedMatrix[2])), // Near
};
// 절두체 선언
Frustum frustumFromMatrix(frustumPlanesFromMatrix);
// AABB 바운딩 영역 가져오기
Box boxBound = mesh.GetBoxBound();
// 바운딩 영역을 사용해 절두체 컬링을 구현
auto checkResult = frustumFromMatrix.CheckBound(boxBound);
if (checkResult == BoundCheckResult::Outside)
{
continue;
}
else if (checkResult == BoundCheckResult::Intersect)
{
// 겹친 게임 오브젝트를 빨간색으로 그림
finalColor = LinearColor::Red;
}
// 메시 그리기
DrawMesh3D(mesh, finalMatrix, finalColor);
}
...
}
AABB 바운딩 볼륨은 구 바운딩 볼륨에 비해 계산량은 많지만, 좀 더 정교하게 절두체 컬링을 수행할 수 있기 때문에 게임 엔진에서 보편적으로 활용된다.
'게임 수학 > 이득우의 게임 수학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 복소수(Complex number) (0) | 2023.05.25 |
|---|---|
| 삼각형 클리핑(Triangle clipping) (0) | 2023.05.24 |
| 바운딩 볼륨(Bounding volume) (0) | 2023.05.22 |
| 원근 투영 행렬로부터 평면의 방정식 만들기 (0) | 2023.05.21 |
| 절두체 컬링(Frustum Culling) (0) | 2023.05.20 |
