
Level 1. 부족한 금액 계산하기 #include #include using namespace std; long long solution(int price, int money, int count) { return max(0, price * count * (count + 1) / 2 - money); }

Level 1. 신규 아이디 추천 디버깅이 수월하도록 각 단계를 함수로 나눴다. string은 다양한 자료구조 함수를 지원하기 때문에 문자열보다는 자료구조처럼 활용했다. step3()에서 unique() 함수를 저렇게 활용하면 연속된 문자를 제거할 수 있다. #include #include #include using namespace std; void step1(string& s) { transform(s.begin(), s.end(), s.begin(), [](char c) { return isalpha(c) ? tolower(c) : c; }); } void step2(string& s) { auto it = remove_if(s.begin(), s.end(), [](char c) { return !..
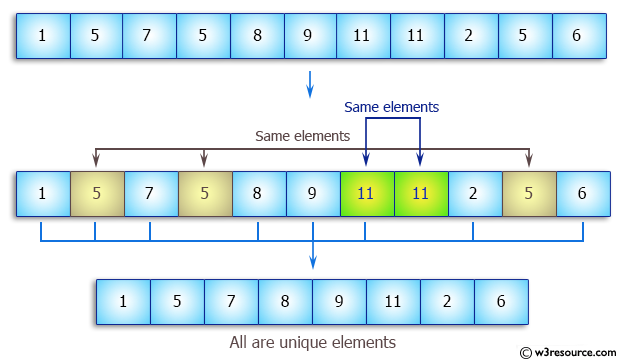
unique가 실행될 때 각 원소는 자신의 양 옆 원소와 비교하여 중복을 제거한다. 그러므로 연속값 제거가 아니라 중복 제거를 원한다면 정렬된 상태에서 사용해야 한다. O(n)에 수행된다. 버블 정렬과 비슷한 방식이며 뒤로 몰아 놓은 중복 원소들의 시작 지점 반복자를 반환한다. #include #include #include using namespace std; void print(vector v); void main() { vector v{5, 4, 1, 1, 1, 3, 2, 2, 7, 6, 6, 8}; cout

Level 1. 크레인 인형뽑기 게임 큐의 배열을 이용해 인형 뽑기 머신을 클래스로 추상화시켜 해결했다. 어려운 문제는 아니었고 카카오에서 내는 시뮬레이션 문제 중에 재밌는 것들이 많은 것 같다. #include #include #include #include using namespace std; class ClawMachine { private: vector board; public: ClawMachine(vector& board) : board(vector(board.size())) { for (vector row : board) for (int i = 0; i board[i].emplace(row[i]); } int pull(int ..

strchr()는 C 스타일 함수이기 때문에 string의 경우 c_str() 함수로 sz(String terminated w/ Zero) 형식으로 변환해주어야 한다. #include #include using namespace std; void main() { string s = "Hello World !!"; // "Hello World !!" 문자열에서 문자 'o'를 검색한다. if (strchr(s.c_str(), 'o') != nullptr) cout

Level 1. 키패드 누르기 어렵지도 않고 보자마자 어떻게 구현해야 할지 감이 잡혀서 꽤 재밌는 문제였다. 이차원 좌표를 저장하는 Pos 구조체를 만들고 연산자 오버로딩을 이용해 각 번호의 거리를 계산하는 함수를 구현해 해결했다. #include #include using namespace std; struct Pos { int x; int y; int operator - (const Pos& p) { return abs(x - p.x) + abs(y - p.y); } }; Pos position(int key) { key = (key == 0) ? 11 : key; return Pos{--key % 3, key / 3}; } int distance(int x, int y) { return positi..