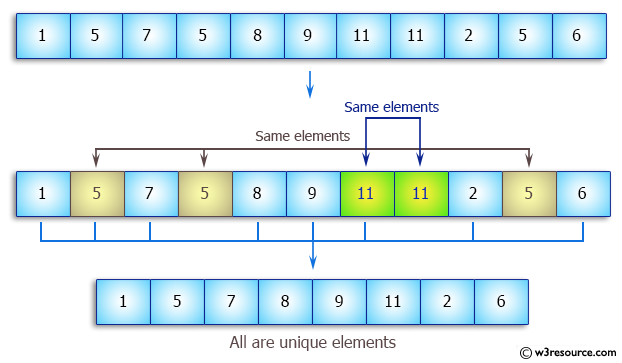
unique가 실행될 때 각 원소는 자신의 양 옆 원소와 비교하여 중복을 제거한다.
- 그러므로 연속값 제거가 아니라 중복 제거를 원한다면 정렬된 상태에서 사용해야 한다.
- O(n)에 수행된다.
- 버블 정렬과 비슷한 방식이며 뒤로 몰아 놓은 중복 원소들의 시작 지점 반복자를 반환한다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void print(vector<int> v);
void main()
{
vector<int> v{5, 4, 1, 1, 1, 3, 2, 2, 7, 6, 6, 8};
cout << "제거 전: ";
print(v);
vector<int>::iterator it = unique(v.begin(), v.end());
v.erase(it, v.end());
cout << "제거 후: ";
print(v);
}
출력
제거 전: 5 4 1 1 1 3 2 2 7 6 6 8
제거 후: 5 4 1 3 2 7 6 8
pred 비교 함수를 다음과 같이 지정해 특정 값의 연속만 제거할 수도 있다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void print(vector<int> v);
void main()
{
vector<int> v{5, 4, 1, 1, 1, 3, 2, 2, 7, 6, 6, 8};
cout << "제거 전: ";
print(v);
// 연속된 1만 제거한다.
auto pred = [](int a, int b) { return a == 1 && b == 1; };
vector<int>::iterator it = unique(v.begin(), v.end(), pred);
v.erase(it, v.end());
cout << "제거 후: ";
print(v);
}
출력
제거 전: 5 4 1 1 1 3 2 2 7 6 6 8
제거 후: 5 4 1 3 2 2 7 6 6 8'자료구조 & 알고리즘 > 기타' 카테고리의 다른 글
| bool 변수는 레퍼런스 전달이 불가능하다. (0) | 2023.03.14 |
|---|---|
| std::replace (0) | 2023.03.14 |
| 문자열에서 문자를 검색하는 strchr() (0) | 2023.03.04 |
| 공백 관련 처리 (0) | 2023.03.02 |
| istream의 기능들 (0) | 2023.03.02 |
