
Level 0. 등수 매기기 평균 점수를 저장하는 벡터1, 역순 정렬된 상태로 저장하는 벡터2를 만들어 해결하였다. 시작 주소부터 원소까지의 거리에 1을 더하면 등수가 된다. #include #include #include using namespace std; vector solution(vector score) { vector answer; vector vec1, vec2; for (const vector& v : score) vec1.emplace_back((v[0] + v[1]) * 0.5); vec2 = vec1; sort(vec2.rbegin(), vec2.rend()); for (const float& average : vec1) answer.emplace_back(find(vec2.begin..

Level 0. 평행 두 선분이 평행하다는 것은 기울기가 같다는 뜻이다. 2중 for문을 이용해 조합을 만들고 vector에 기울기를 저장하여 매번 비교하는 식으로 해결했다. 하지만, 2중 for문 안에 find 함수가 있기 때문에 사실상 O(n³)의 복잡도를 갖는다. #include #include #include using namespace std; int solution(vector dots) { vector slopes; for (auto it = dots.begin(); it < dots.end() - 1; ++it) { for (auto jt = it + 1; jt < dots.end(); ++jt) { float x1 = (*it)[0], y1 = (*it)[1]; float x2 = (*j..
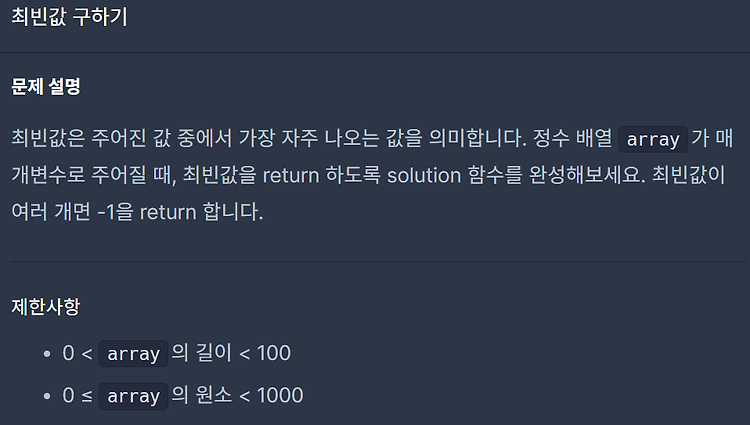
Level 0. 최빈값 구하기 첫 번째 풀이 map 내의 키가 정렬된 상태를 유지할 필요가 없기 때문에 레드-블랙 트리를 사용하는 map보다는 해시 테이블을 사용하는 unordered_map을 사용했다. 개수가 최대인 pair를 찾고 최댓값이 여러 개인지 확인하여 해결했다. 최댓값을 찾는 부분에서 O(n), 최댓값과 같은 값이 찾는 부분에서 O(n)이 소요되기 때문에 원소들을 2번 순회해야 한다. #include #include #include #include using namespace std; int solution(vector array) { int answer = 0; unordered_map umap; for (int num : array) ++umap[num]; unordered_map::it..

Level 0. 다음에 올 숫자 #include #include using namespace std; int solution(vector common) { int diff = common[1] - common[0]; return (diff == common[2] - common[1]) ? common.back() + diff : common.back() * (common[1] / common[0]); } 특별한 것은 없었던 문제다. 첫 번째, 두 번째, 세 번째 원소를 확인해 등차수열인지 확인하고 마지막 원소에 등차를 더하거나 등비를 곱해 해결한다.
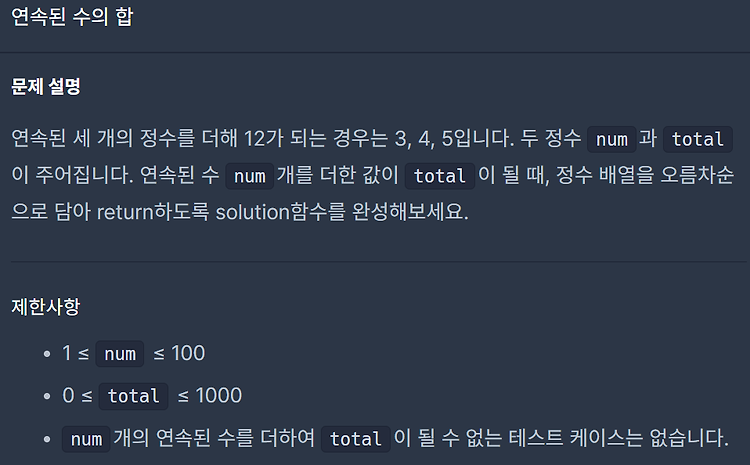
Level 0. 연속된 수의 합 #include #include using namespace std; vector solution(int num, int total) { vector answer(num, total / num - (num - 1) / 2); for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) answer[i] += i; return answer; } 시작 = 평균 - (개수 - 1) / 2 시작 값을 num 개수만큼 만들고 index 별로 증가시켜준다.

Level 0. 종이 자르기 #include using namespace std; int solution(int M, int N) { return M * N - 1; } (가로 - 1) + 가로 * (세로 - 1) = (M - 1) + M * (N - 1) = M * N - 1