코딩 테스트를 위한 자료 구조와 알고리즘 with C++
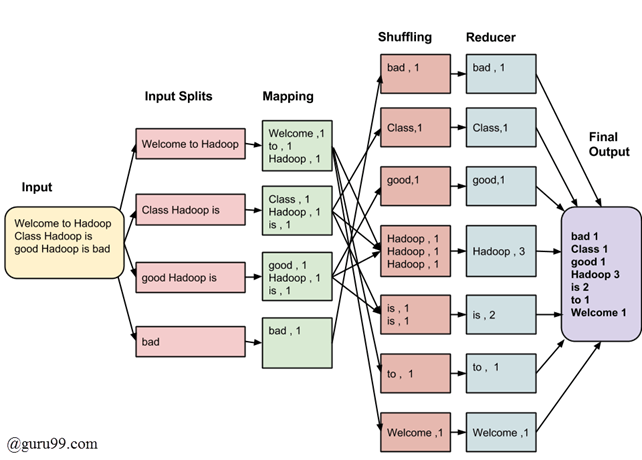
맵리듀스
대규모 데이터셋을 생성하고 처리하기 위한 프로그래밍 모델 및 구현이다.
(키, 값) 쌍을 처리해 중간 단계의 (키, 값) 쌍을 생성하는 Map
모든 중간 단계 키에 해당하는 값을 병합하는 Reduce
맵리듀스의 실제 사용 예
- 하둡(Hadoop)
Map 연산의 예
- 컨테이너의 모든 원소에 f(x)를 적용하는 연산이다.
- f(x) = x²
void map_example(vector<int> S)
{
auto Fx = [](int& x) { x = pow(x, 2); };
for_each(S.begin(), S.end(), Fx);
}
Reduce 연산의 예
- 컨테이너의 모든 원소에 f(acc, x)를 적용하여 하나의 값으로 축약하는 연산이다.
- f(acc, x) = acc + x
// std::accumulate()는 누적합 연산을 하기 때문에 제한된 형태의 Reduce이다.
int reduce_example(vector<int> S)
{
auto Facc_x = [](int acc, int x) { return acc + x; };
return accumulate(S.begin(), S.end(), 0, Facc_x);
}// std::reduce() 함수는 C++17부터 지원된다.
int reduce_example(vector<int> S)
{
return reduce(S.begin(), S.end());
}
C++에서의 Map
std::transform()
- Map 연산을 수행한 결과를 다른 컨테이너에 저장한다.
- 순차적으로 수행됨을 보장하지 않는다.
std::for_each()
- Map 연산을 수행한다.
- Func에서 원소를 참조 형식으로 받으면 직접 값을 수정할 수 있으나, for_each()에서 원소의 값을 변경하는 것은 권장되지 않는다.
- 순차적으로 수행됨을 보장한다.
C++에서의 Reduce
std::accumulate()
- Reduce 연산을 수행하여 값을 반환한다.
- 실제로는 누적합 연산이기 때문에 제한된 형태의 Reduce이다.
std::reduce()
- C++17부터 지원하는 Reduce 연산이다.
- 병렬 처리를 지원한다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
void transform_test(vector<int> S)
{
vector<int> Tr;
auto Fx_transform = [](int x) { return pow(x, 2); };
auto Fx_for_each = [](int& x) { x = pow(x, 2); };
cout << "[맵 테스트]" << endl;
cout << "입력 배열, S: ";
for (int x : S) cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
// std::transform()
transform(S.begin(), S.end(), back_inserter(Tr), Fx_transform);
cout << "std::transform(), Tr: ";
for (int fx : Tr) cout << fx << " ";
cout << endl;
// std::for_each()
for_each(S.begin(), S.end(), Fx_for_each);
cout << "std::for_each(), S: ";
for (int fx : S) cout << fx << " ";
cout << endl;
}
void reduce_test(vector<int> S)
{
cout << endl << "[리듀스 테스트]" << endl;
cout << "입력 배열, S: ";
for (int x : S) cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
// std::accumulate()
int ans = accumulate(S.begin(), S.end(), 0, [](int acc, int x) { return acc + x; });
cout << "std::accumulate(), ans: " << ans << endl;
#if ((defined(_MSVC_LANG) && _MSVC_LANG >= 201703L) || __cplusplus >= 201703L)
// std::reduce()
ans = reduce(S.begin(), S.end());
cout << "std::reduce(), ans: " << ans << endl;
#endif
}
void main()
{
vector<int> S{1, 10, 4, 7, 3, 5, 6, 9, 8, 2};
transform_test(S);
reduce_test(S);
}
출력
[맵 테스트]
입력 배열, S: 1 10 4 7 3 5 6 9 8 2
std::transform(), Tr: 1 100 16 49 9 25 36 81 64 4
std::for_each(), S: 1 100 16 49 9 25 36 81 64 4
[리듀스 테스트]
입력 배열, S: 1 10 4 7 3 5 6 9 8 2
std::accumulate(), ans: 55
std::reduce(), ans: 55'자료구조 & 알고리즘 > 코딩 테스트를 위한 자료 구조와 알고리즘 with C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 최단 작업 우선(SJF) 스케줄링 (0) | 2023.02.22 |
|---|---|
| 탐욕법(Greedy Algorithm) (0) | 2023.02.22 |
| 분할 정복 관련 STL 함수들 (0) | 2023.02.20 |
| 병합 정렬(Merge Sort) (0) | 2023.02.17 |
| 이진 검색(Binary Search) (0) | 2023.02.16 |
